Heap and Heap Sort
The heap sort uses the “Complete Binary Tree” to maintain the data structure. In the heap sort, there are two common heap sorts: one is “minimum heap”, and the other is “maximum heap”. The idea of these two is that the root node of the binary tree will be the minimum or the maximum of all nodes.
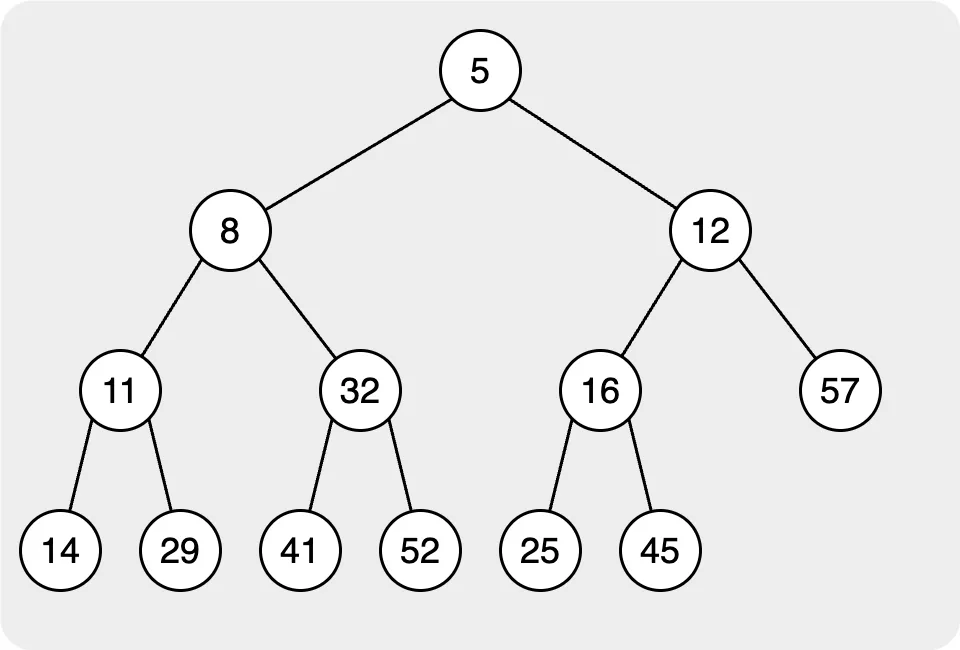
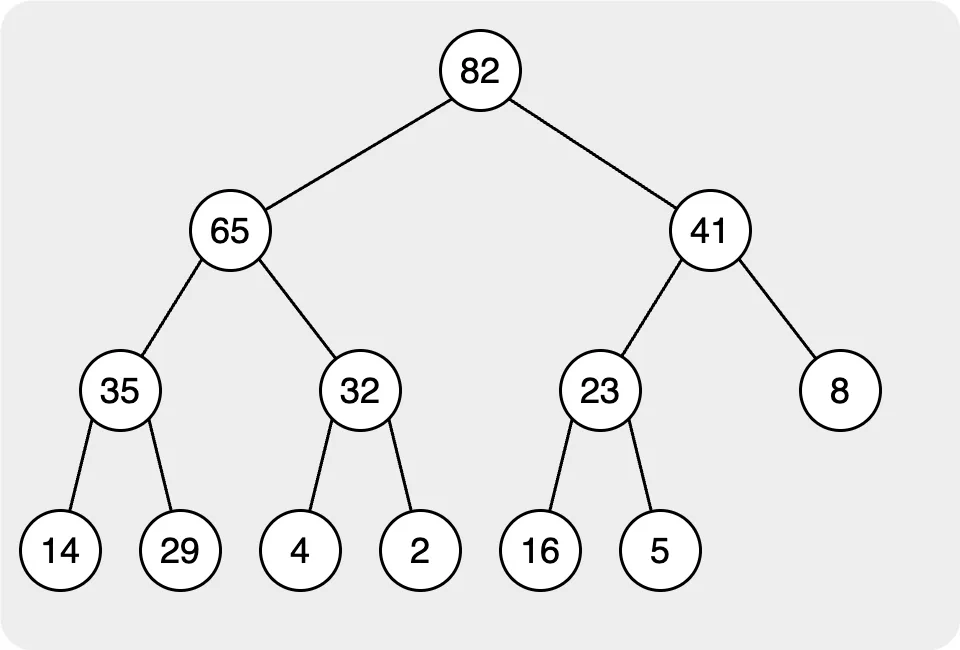
Maintain a Heap
For the following, I will use the maximum heap for the demonstration. In the heap, we will focus on two behaviors insert and pop max/min.
Insert
The first step for building the max/min heap is inserting all nodes into the heap and making those nodes comply with the rule. In a heap, we usually use the complete binary tree to maintain the data structure; when there is a node that needs to be inserted into the tree, it needs to be the last layer and aligned to the left.
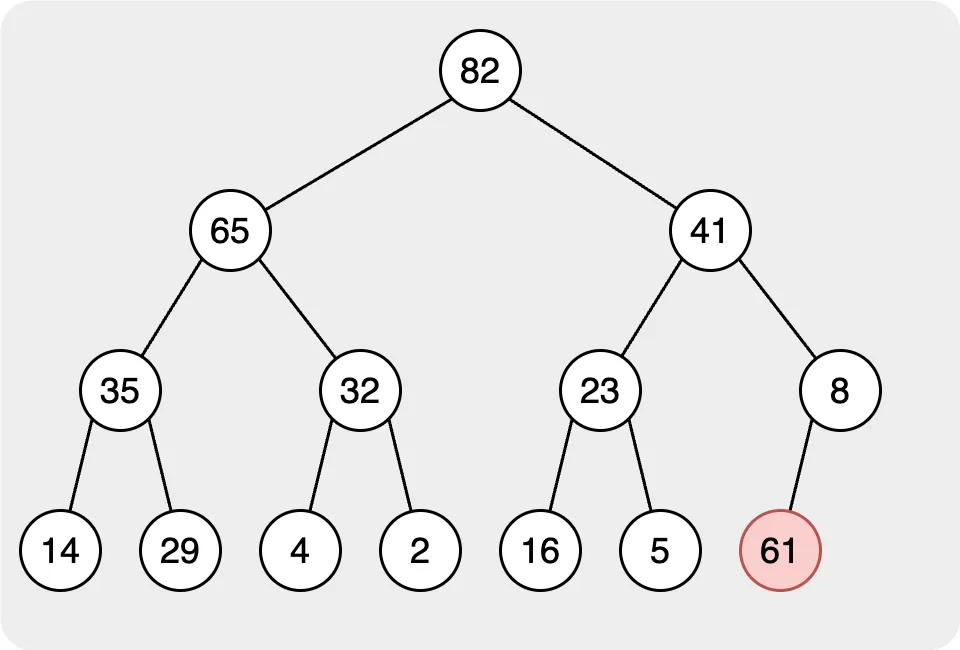
After inserting the node into a heap, we must let the node follow the rule. In the maximum heap, all parent nodes’ values need to be larger than the children nodes. Therefore, we need to compare the node value we insert with its parent. If the parent node’s value is smaller than the child’s, we need to switch them. Then, keep comparing the value until the root node.
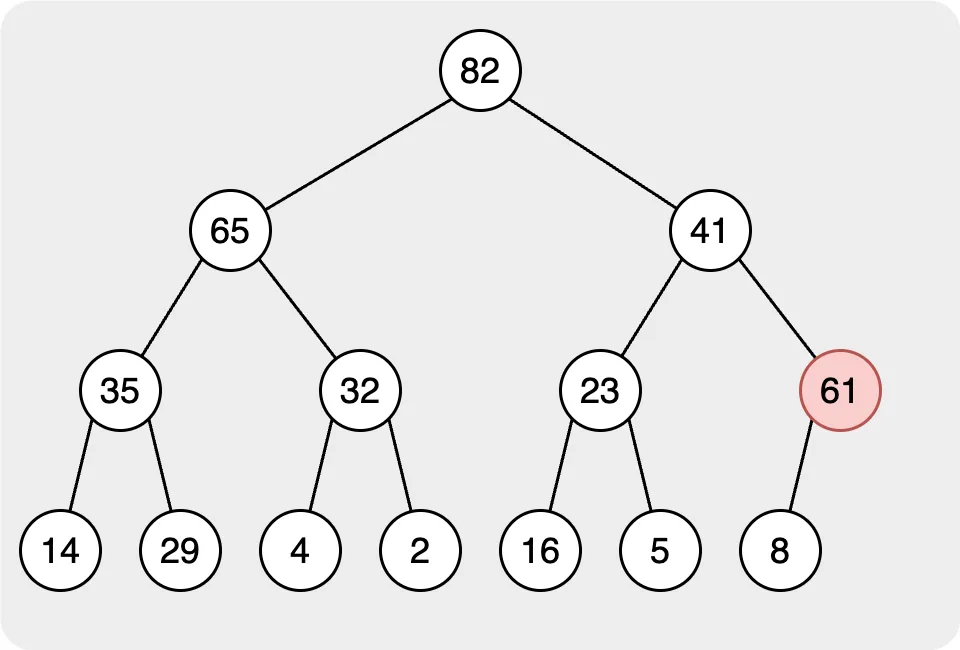
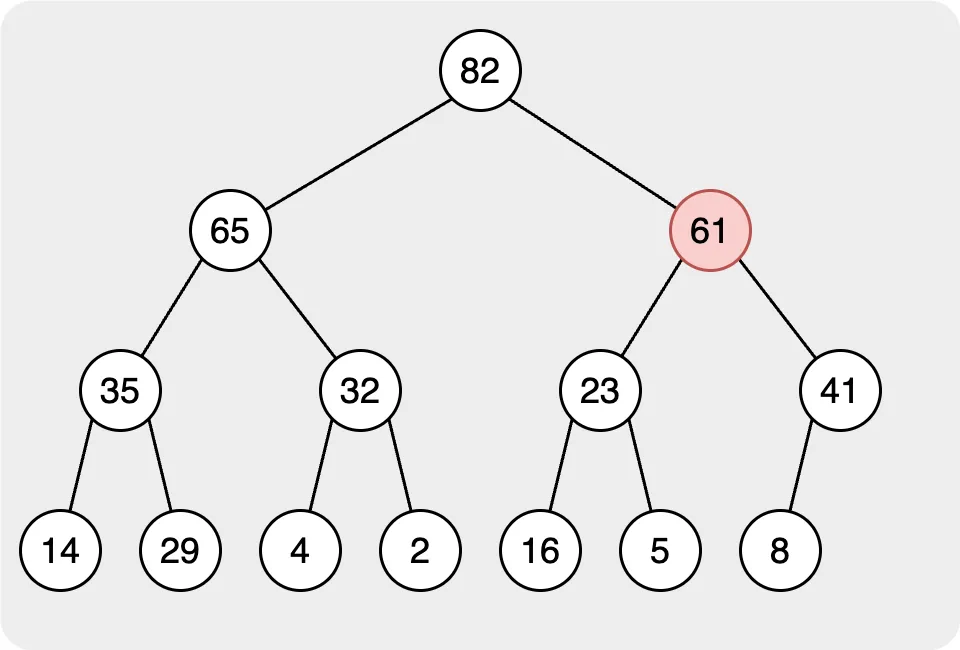
In the image above, we can see that we add the node with the value 61. First, we add the node to the last layer and align it to the left. Second, we need to let the node we added follow the rule of the max heap. We need to let the value of the parent node be larger than the child node. Therefore, we start to compare the value from the node we added to the root; if the child is larger than the parents, we need to switch them. Finally, when we check the node to the root, you will find that all the nodes in the heap are following the rule. It also means that the while inserting is finished.
Pop
In the max/min heap, we will use the pop to get the max/min node in the heap. After we remove the max/min node in the heap, there will be no root node. So, we need to rearrange the heap to allow it to follow the rules of the heap.
When we want to remove the root node, which represents the max/min node in the heap, we will move the leftest node in the last layer as the root node. Then rearrange the heap.
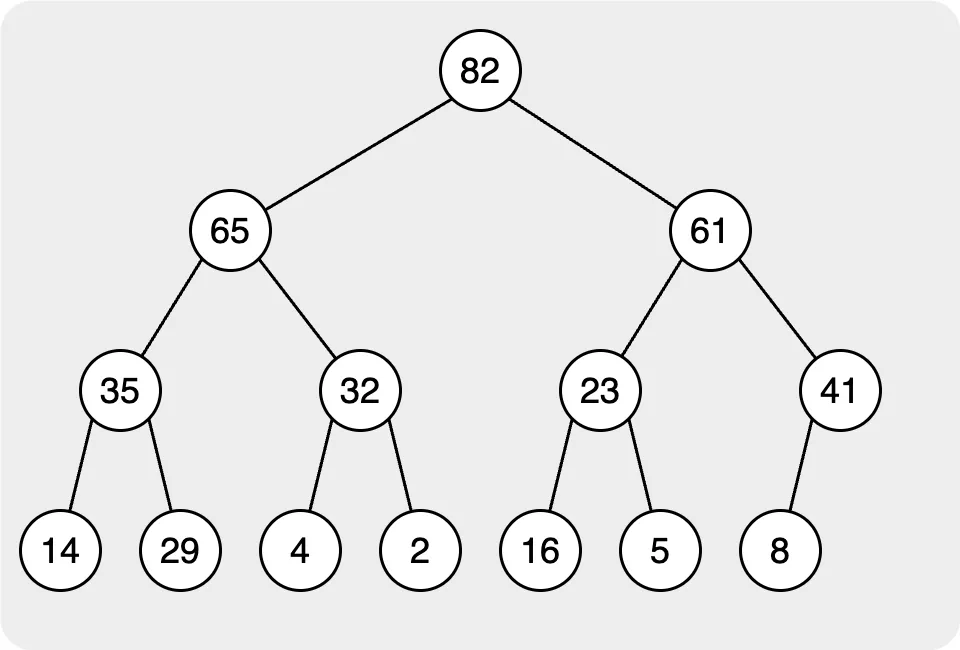
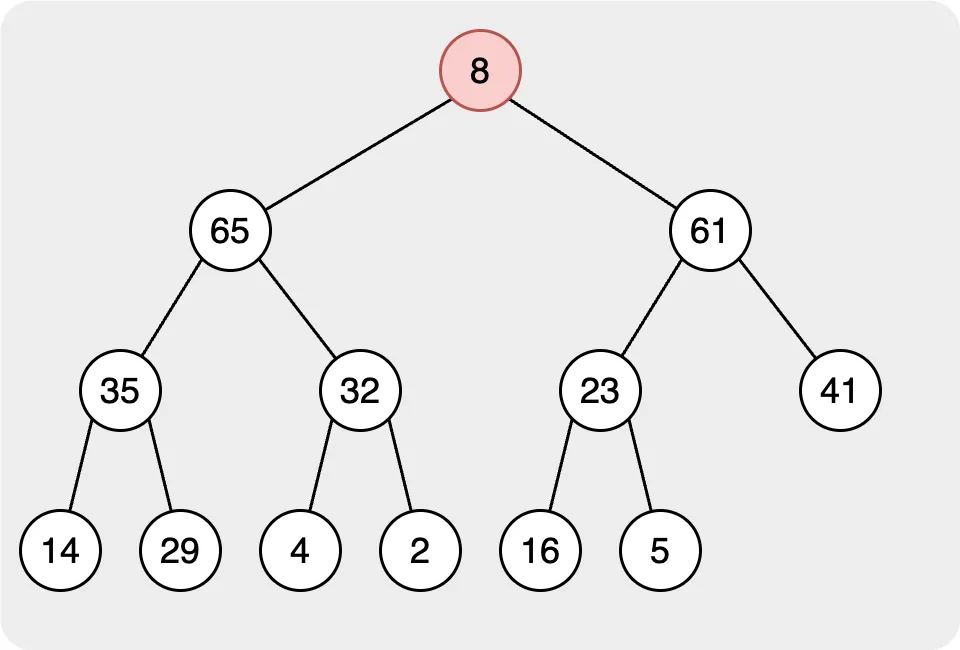
In the second step, we need to find the correct place for the root node. In this step, we will compare the target node to its children. If the value of the target node is smaller than the children’s, we will swap with the node with the largest value node Then, continue to compare the nodes until all nodes follow the rule.
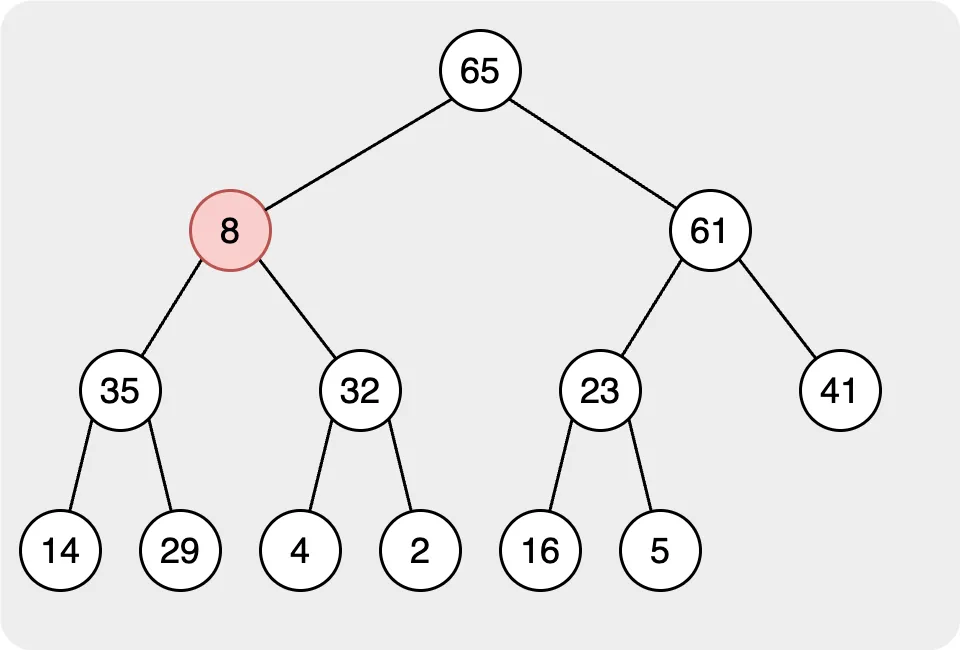
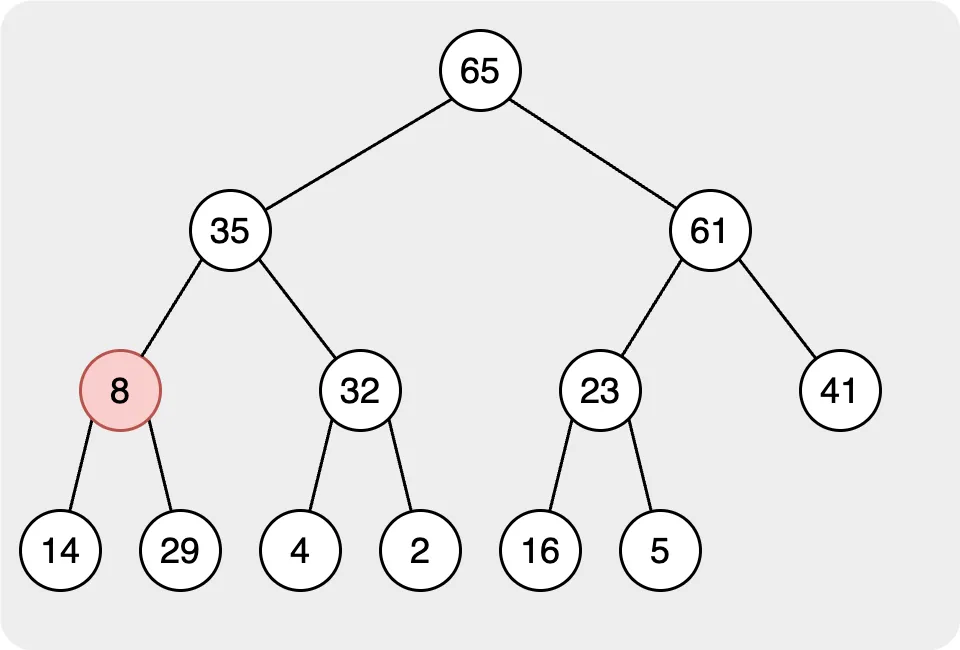
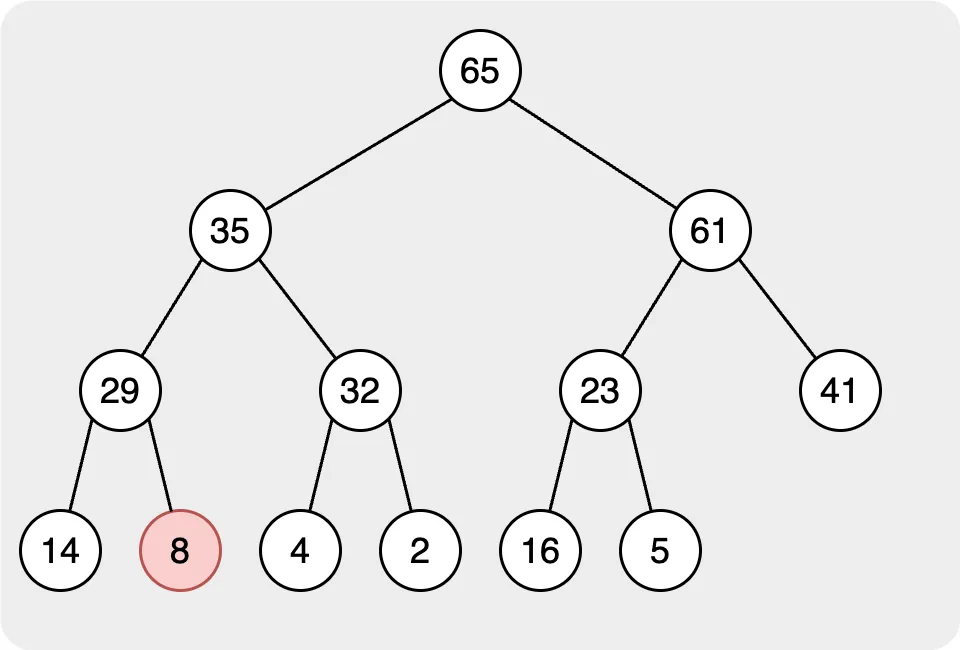
Until all the target nodes and their children follow the rule, we finish all steps in the pop behavior.
Heap Sort
When we know what is the heap, the heap sort is also a very common sorting people will use. Because for building the heap, when inserting a node, we only spend O(logn) time rearranging the heap. So, the total time of the heap sort will be O(nlogn).
When using the heap sort, it means we put all unsorted numbers into the heap and build the max/min heap. To get the result, just pop out the nodes in order, and we can get the sorted number.
Data Structure Container in Heap
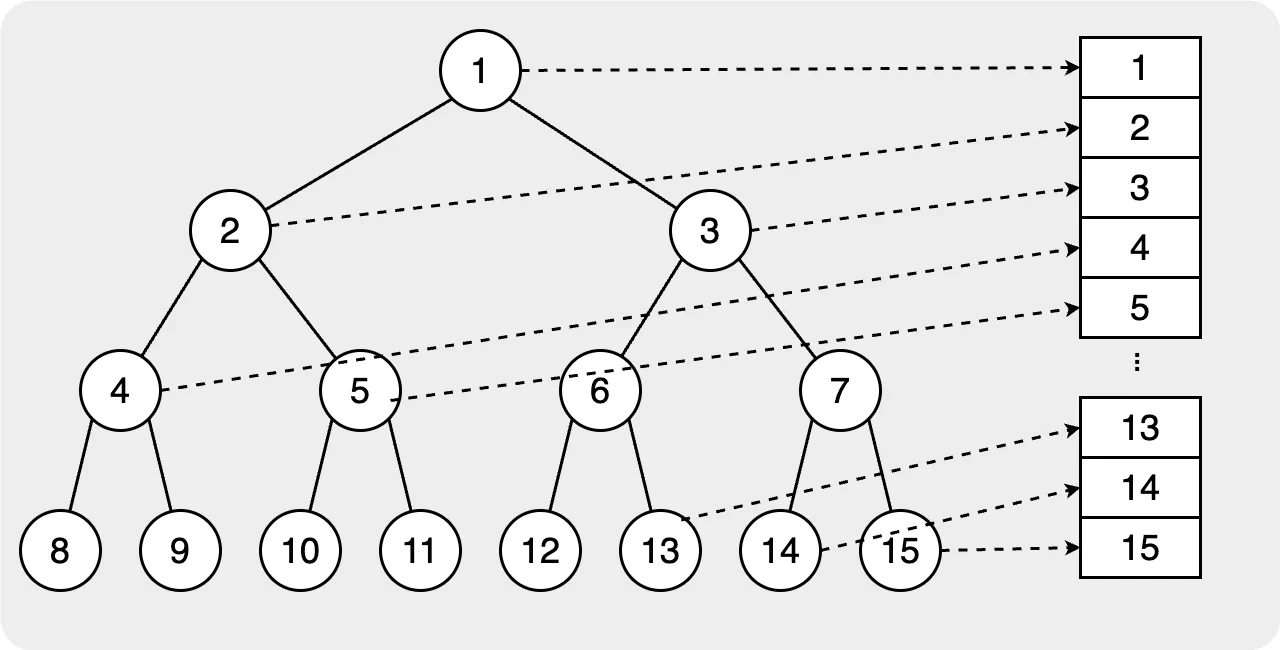
As we talk above, the heap usually uses the complete binary tree to maintain the heap. However, in programming, it is not easy to implement and maintain the binary tree. We usually change the binary tree into the vector for easy maintenance. For changing the binary tree to the vector, first, we need to get all nodes’ indexes and their relationship.
In this situation, we always let the index start from one, and in the binary tree, it will start from root to leaf and left to right. So, the index of each node will be like the image below.
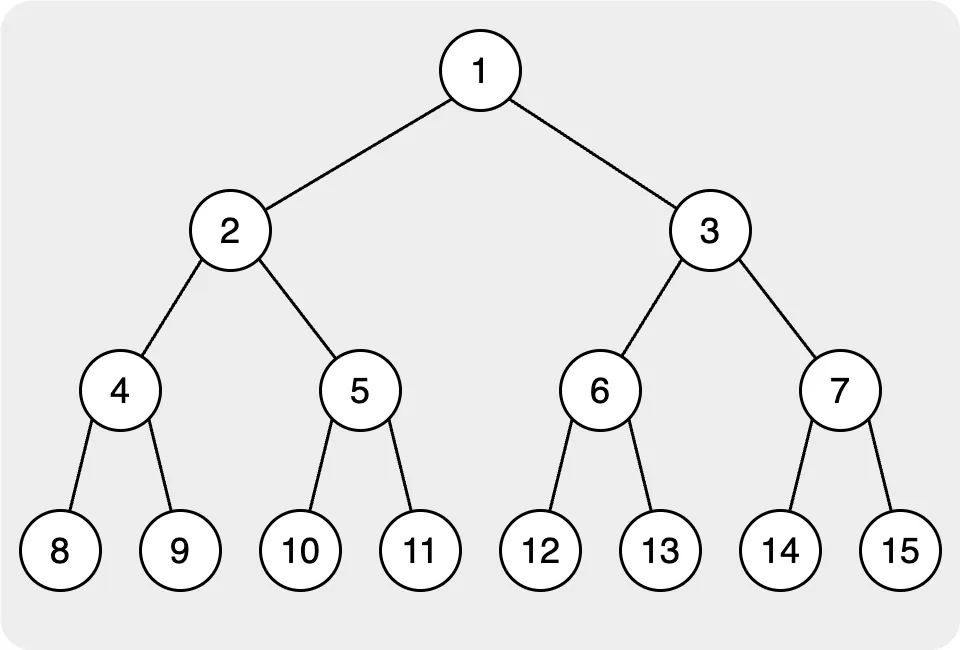
As the image above shows the index of the left child will be 2 * idx and the right child will be 2 * idx + 1; it will help us easily find the child node when we use the vector. Then, if we want to get the parent node’s idx, it will be floor(idx / 2). In this way, we can use the index to find the parent node or the children node very quickly.
Heap in C++
When understanding the concept of the heap, for the people using C++, there is an STL container for us to use the heap. In this section, we will introduce how to use the heap in C++.
In C++, the priority_queue is implemented by the heap. As the default, if we only set the type of data of priority_queue, it will be set as the maximum heap. And the default container of the priority_queue is the vector. If you want to change the maximum heap to the minimum heap, you can use the build-in Compare call greater<T> to set the priority_queue to the minimum heap.
The Compare parameter is defined such that it returns true if its first argument comes before its second argument in a weak ordering. But because the priority queue outputs the largest elements first, the elements that “come before” are actually output last. - By cppreference.com
Common member function in heap:
push(): insert the element and sortpop(): remove the top elementtop(): access the top elementempty(): check whether the heap is empty or notsize(): return the number of the elements
If you want to design your compare funstion, please check out the cppreference.com for detail information.
If you have any questions, please feel free to leave some comments or contact me by Email. Thank you.
![Featured image of post [Note] Heap and Heap Sort](/posts/alg-heap/img/cover_hu31b8df77b0b5af2ce03ad4e274285f7c_763578_800x0_resize_q75_h2_box_2.webp)